How to operate a drone? It’s a question many ask, as these versatile machines offer exciting possibilities from aerial photography to surveying. Mastering drone operation requires understanding not only the controls but also crucial safety procedures, legal regulations, and essential maintenance practices. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of these aspects, empowering you to confidently and responsibly take to the skies.
From pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvering techniques, we’ll cover everything you need to know to become a proficient drone pilot. We’ll explore different flight modes, camera settings for optimal image capture, and essential troubleshooting steps. Safety and legal compliance are paramount, and we’ll address these crucial aspects throughout the guide.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before embarking on any drone flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for ensuring both the safety of the drone and the surrounding environment. Neglecting these checks can lead to accidents, damage to the drone, and potential harm to people or property. This section Artikels essential pre-flight procedures and safety considerations.
Pre-Flight Checklist
A comprehensive pre-flight checklist should be followed diligently before each flight. This checklist ensures all systems are functioning correctly and minimizes the risk of unforeseen problems during operation.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to get started is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. From pre-flight checks to mastering flight maneuvers, this guide provides the necessary knowledge for safe and responsible drone operation.
- Battery Check: Verify the battery level is sufficient for the planned flight duration. Inspect the battery for any signs of damage, such as swelling or leakage.
- Propeller Inspection: Carefully examine each propeller for cracks, chips, or any signs of damage. Replace damaged propellers immediately.
- GPS Signal Acquisition: Ensure the drone has acquired a strong GPS signal before takeoff. This is crucial for accurate positioning and stability, especially in GPS-dependent flight modes.
- Gimbal Check (if applicable): If your drone has a gimbal, ensure it’s properly calibrated and functioning correctly. Check for smooth movement and accurate stabilization.
- Visual Inspection: Conduct a visual inspection of the entire drone, checking for any loose parts, damage, or obstructions.
- Environmental Assessment: Check weather conditions (wind speed, precipitation), assess the airspace for potential hazards (power lines, trees, buildings), and ensure sufficient visibility.
Pre-Flight Safety Procedures
Adhering to established safety procedures is paramount for responsible drone operation. The following table summarizes key procedures and their importance.
| Procedure | Importance | Consequences of Neglect |
|---|---|---|
| Battery Check | Ensures sufficient power for the flight, preventing mid-flight power failure. | Unexpected power loss leading to uncontrolled descent and potential damage. |
| Propeller Inspection | Identifies damaged propellers that could cause instability or failure during flight. | Propeller failure resulting in loss of control and potential damage or injury. |
| GPS Signal Acquisition | Ensures accurate positioning and stable flight, especially in autonomous modes. | Inaccurate positioning, unstable flight, and potential collisions with obstacles. |
| Environmental Assessment | Identifies potential hazards and adverse weather conditions that could affect flight safety. | Collisions with obstacles, damage to the drone due to weather, or accidents involving people. |
Safe Drone Operation Near People and Obstacles
Maintaining a safe distance from people and obstacles is vital. Always keep the drone within your line of sight and avoid flying over crowds or congested areas. Prioritize safe operation above all else.
- Maintain a safe distance from people and property.
- Avoid flying over crowds or congested areas.
- Always keep the drone within visual line of sight.
- Be aware of your surroundings and potential hazards.
- Never fly under the influence of drugs or alcohol.
Understanding Drone Controls and Flight Modes
Understanding your drone’s controls and flight modes is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section details the calibration process and explains different flight modes and their applications.
Drone Control Calibration
Proper calibration is essential for accurate and predictable drone control. The specific steps may vary depending on the drone model, but generally involve the following:
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Place the drone on a level surface.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for calibrating the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Perform a pre-flight check as described previously.
- Once calibration is complete, the drone should be ready for takeoff.
Drone Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. Understanding their functionalities is crucial for adapting to different flying conditions.
- GPS Mode: Relies on GPS signals for position holding and stable flight. Ideal for outdoor flying in open spaces.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains the drone’s orientation relative to its starting position, regardless of GPS signal strength. Useful for indoor flights or areas with weak GPS signals.
- Manual Mode (or similar): Provides direct control over the drone’s movements. Requires more skill and experience.
Comparison of Flight Modes
The choice of flight mode depends on the specific flying environment and pilot experience. GPS mode offers stability but is reliant on a strong GPS signal. Attitude mode is useful in GPS-challenged environments but requires more pilot skill. Manual mode offers maximum control but is the most challenging.
| Flight Mode | Advantages | Disadvantages | Suitable Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS Mode | Stable flight, precise positioning | Requires strong GPS signal | Open spaces, outdoor flying |
| Attitude Mode | Stable orientation, usable with weak GPS | Less precise positioning | Indoor flying, areas with weak GPS |
| Manual Mode | Maximum control | Requires significant skill | Experienced pilots, specific maneuvers |
Drone Controller Functions
A typical drone controller has several sticks and buttons, each with a specific function. Understanding these controls is essential for safe and effective operation.
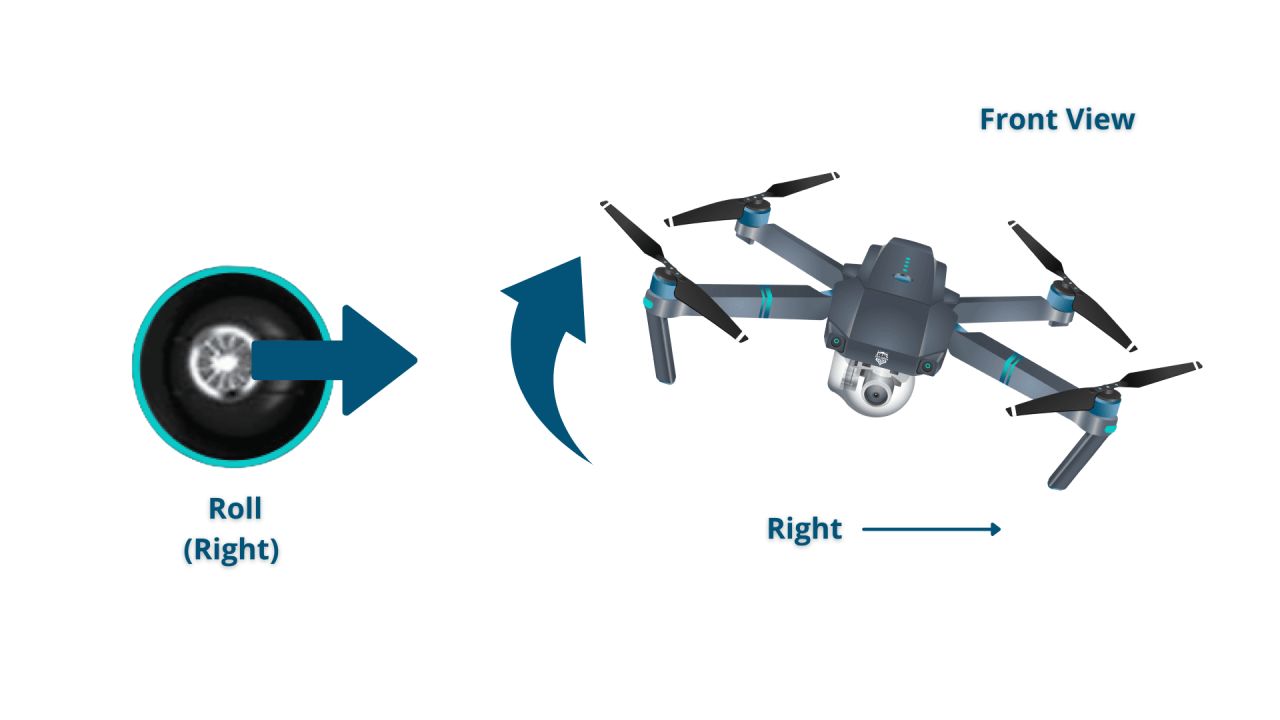
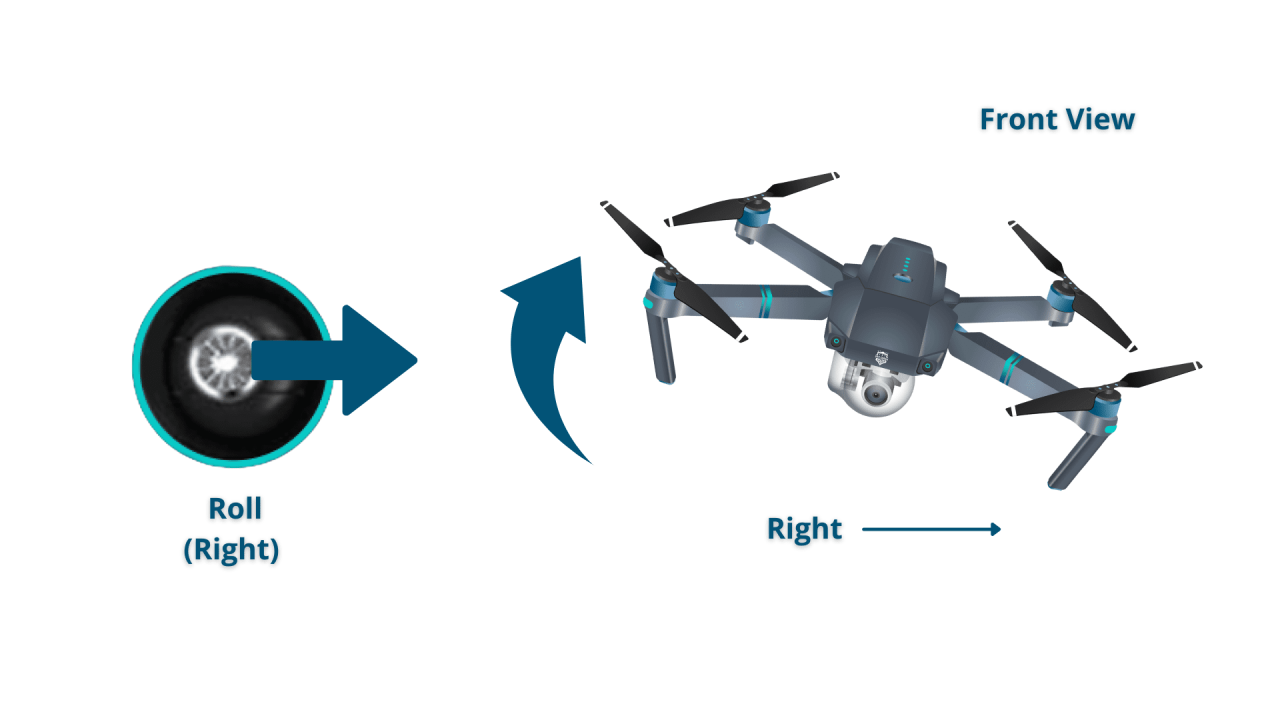
- Left Stick: Controls the drone’s yaw (rotation) and throttle (altitude).
- Right Stick: Controls the drone’s pitch (forward/backward movement) and roll (left/right movement).
- Return to Home (RTH) Button: Initiates an automated return to the home point.
- Emergency Stop Button: Cuts power to the motors, bringing the drone to an immediate stop.
- Camera Control Buttons: Allow for adjustments to camera settings (e.g., zoom, photo/video recording).
Taking Off, Hovering, and Landing
The takeoff, hovering, and landing procedures are critical stages of a drone flight. These steps, if performed correctly, ensure a smooth and safe flight.
Safe Takeoff Procedure
A smooth and controlled takeoff minimizes the risk of accidents. The steps generally involve:
- Ensure the drone is fully calibrated and has a strong GPS signal.
- Slowly increase the throttle to lift the drone off the ground.
- Maintain a slow and steady ascent.
- Once at the desired altitude, hover steadily before proceeding to other maneuvers.
Stable Hovering
Maintaining a stable hover requires precise control and adjustments to the throttle and directional controls. The drone should remain stationary at a specific altitude and location.
Safe Landing Procedure

A controlled landing prevents damage to the drone and ensures a safe conclusion to the flight.
- Slowly decrease the throttle to begin descent.
- Maintain a slow and steady descent.
- As the drone approaches the ground, reduce the throttle further.
- Gently set the drone down on a level surface.
Step-by-Step Flight Guide (with Image Descriptions)
Each stage of a flight requires specific actions and careful attention to detail.
- Takeoff: Image Description: The drone is shown lifting smoothly off the ground, with propellers spinning steadily and the drone maintaining a level orientation. The surrounding environment is visible, showing a clear and safe takeoff area.
- Hovering: Image Description: The drone is shown hovering steadily at a specific altitude, remaining perfectly stationary. The image emphasizes the drone’s stable position and lack of movement.
- Maneuvering: Image Description: The drone is shown smoothly moving through the air, executing a planned maneuver. The image highlights the drone’s controlled and precise movements.
- Landing: Image Description: The drone is shown descending gently towards the ground, with the propellers slowing down gradually. The drone is shown landing smoothly and softly on a level surface.
Drone Navigation and Maneuvering
Effective drone navigation involves understanding different techniques and adapting to various environments. This section explores navigation techniques, challenges, and advanced maneuvers.
Navigation Techniques
Navigating a drone effectively involves understanding the environment and utilizing appropriate techniques. In open spaces, GPS-assisted navigation is often sufficient. In confined areas, visual navigation and obstacle avoidance become more crucial.
Navigation Challenges and Solutions
Several challenges can impact drone navigation. GPS signal loss, for instance, can be mitigated by using alternative navigation systems (optical flow, visual inertial odometry). Strong winds can affect stability, requiring adjustments in control inputs. Obstacles require careful planning and maneuvering.
Advanced Maneuvering Techniques
Advanced maneuvering involves precise control and understanding of the drone’s capabilities. This includes techniques such as precise movements, aerial photography maneuvers (circling, tracking), and coordinated flight patterns.
Drone Navigation Systems Comparison
Different navigation systems offer varying levels of accuracy and reliability. GPS relies on satellite signals, while optical flow uses camera data to determine movement. Each system has advantages and disadvantages depending on the environment.
| Navigation System | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| GPS | High accuracy in open areas, long range | Relies on satellite signals, susceptible to interference |
| Optical Flow | Works well in GPS-denied environments | Limited range, accuracy decreases with distance |
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings and composition techniques. This section details how to optimize camera settings and create compelling aerial shots.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Optimizing camera settings is crucial for achieving the desired image quality. Adjustments to ISO, shutter speed, and aperture affect brightness, sharpness, and depth of field.
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos, How to operate a drone

Capturing professional-quality aerial content requires planning and attention to detail. Understanding lighting conditions, choosing the right settings, and employing stable flight techniques are all crucial aspects.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics, from pre-flight checks to maneuvering in different environments, is crucial. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including practical exercises, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Mastering these skills will ensure safe and effective drone operation, ultimately enhancing your aerial capabilities.
Tips for Composing Aerial Shots
Effective composition is key to creating visually appealing aerial shots. Consider elements such as leading lines, rule of thirds, and perspective to create dynamic and engaging images.
Drone Camera Settings and Their Effects
Different camera settings produce varied results. Understanding these effects allows for greater control over image quality.
| Setting | Effect on Image Quality |
|---|---|
| ISO | Controls image sensitivity to light; higher ISO increases brightness but can introduce noise. |
| Shutter Speed | Controls the duration of light exposure; faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds create motion blur. |
| Aperture | Controls the amount of light entering the lens; wider apertures create shallow depth of field, while narrower apertures increase depth of field. |
Battery Management and Charging
Proper battery care is essential for extending the lifespan of your drone batteries and ensuring safe operation. This section Artikels best practices for battery management and charging.
Importance of Proper Battery Care
Following proper battery care procedures ensures optimal battery performance and longevity. Neglecting these procedures can lead to premature battery degradation and potential safety hazards.
Charging and Storing Drone Batteries
Always use the manufacturer-recommended charger and follow the charging instructions carefully. Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight or extreme temperatures.
Signs of Battery Damage and Actions to Take
Signs of battery damage include swelling, leakage, or unusual heating. If any of these signs are observed, immediately discontinue use and dispose of the battery properly.
Best Practices for Maintaining Drone Batteries
Adhering to these best practices ensures optimal battery performance and extends their lifespan.
- Use the manufacturer-recommended charger.
- Avoid overcharging or discharging batteries.
- Store batteries in a cool, dry place.
- Inspect batteries regularly for signs of damage.
- Dispose of damaged batteries properly.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Understanding how to troubleshoot common drone issues is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency. This section provides guidance on resolving common problems.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Several common issues can arise during drone operation. Knowing how to address these problems efficiently is essential.
Troubleshooting Guide
GPS Signal Loss: Check for obstructions, ensure sufficient satellite visibility, and try recalibrating the GPS.
Low Battery: Land the drone immediately, charge the battery, and avoid flying until the battery is fully charged.
Motor Malfunction: Inspect the motors and propellers for damage, and replace any damaged components. If the problem persists, contact the manufacturer for support.
Controller Issues: Check the controller’s battery level, ensure proper connection with the drone, and try recalibrating the controller.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Understanding and adhering to local drone regulations is essential for responsible and legal drone operation. This section Artikels key legal considerations for drone pilots.
Importance of Understanding Drone Regulations
Operating a drone without understanding the relevant regulations can lead to legal consequences, including fines and penalties. It’s crucial to be aware of the laws and regulations in your area before flying.
Airspace Restrictions and Flight Limitations
Various airspace restrictions and flight limitations exist, including restrictions near airports, military bases, and other sensitive areas. These restrictions are designed to ensure safety and security.
Resources for Obtaining Permits and Licenses
Depending on your location and intended use, you may need to obtain permits or licenses before operating a drone. Information on obtaining these permits can typically be found on the website of your local aviation authority.
Essential Legal Considerations for Drone Pilots
Responsible drone operation involves adhering to these legal and ethical considerations.
- Register your drone with the appropriate authorities.
- Obtain necessary permits and licenses.
- Adhere to airspace restrictions and flight limitations.
- Respect the privacy of others.
- Fly responsibly and safely.
Operating a drone is a rewarding experience, offering stunning perspectives and diverse applications. By following the safety guidelines, understanding the technical aspects, and adhering to legal regulations, you can unlock the full potential of your drone. Remember that continuous learning and practice are key to honing your skills and ensuring safe and responsible operation. So, take to the skies, capture breathtaking footage, and explore the world from a new perspective!
Common Queries: How To Operate A Drone
What type of drone is best for beginners?
For beginners, a user-friendly drone with GPS stabilization, obstacle avoidance features, and a relatively simple interface is recommended. Many reputable brands offer excellent entry-level models.
How often should I calibrate my drone?
Calibration is generally recommended before each flight, especially after any significant impact or if you notice erratic behavior. Consult your drone’s manual for specific instructions.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If your drone loses GPS signal, immediately switch to a lower altitude and attempt to regain signal. If unsuccessful, initiate a controlled landing. Never attempt to fly without GPS in challenging environments.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, flight conditions (wind, altitude), and usage. Expect anywhere from 15-30 minutes of flight time per battery charge on average. Always check your specific drone’s specifications.
Where can I find information on local drone regulations?
Your national aviation authority’s website is the best place to find comprehensive information on drone regulations in your area. Additionally, many online resources and drone pilot communities provide valuable information.